Benefits of Exercising
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
27 September 2017
Green Environment
Pursuant to the government effort to create a green environment and to save energy and water nationwide, UTAR strongly encourages the staff/students to save electricity and water in all campuses. Saving electricity and water is a team effort that involves everyone in the campuses.
The following are some tips for your attention:
Conserve Electricity
1. Switch off computers when not in use. Appliances such as computers, TVs, cell phone charger, electronic devices, etc. still consume energy by just being plugged in or when on standby mode. Unplug them when not in use.
2. Do not leave computers at standby mode at the end of the day or over the weekend as this can still draw electricity use. Turn off the monitor and CPU if you are away from office for a period of time.
3. Turn off lights, fans and air conditioners when nobody is in the room.
4. Do not open windows or doors in an air-conditioned room just to avoid being too cold, instead set air-conditioners to suitable level of temperature (such as 24°C or above) as more energy is required to keep the rooms cool.
5. Stop charging mobile device when it is full.
6. Use the stairs instead of lift as it saves electrical energy and also helps train our physical body.
7. Consider the environment before you print to save energy as well as paper.
Conserve Water
1. Report all water leaks immediately.
2. Turn off all taps after use. Do not keep the tap water running unnecessarily.
4. Do not use too much detergent in washing your cups/utensils as more water is needed to wash them clean.
“TOGETHER WE SAVE ENERGY & WATER”
Energy Management Committee
(EGMC)
The Heat Blast
Like it or not, our lives are influenced by weather conditions daily. Hot and dry weather is a common phenomenon in tropical regions like our country. A heat wave is a prolonged period of excessively hot weather, which may be accompanied by high humidity, especially in oceanic climate countries. Exposure to the hot weather is one of the causes that contribute to the
increase of the patients visiting clinics, the number of hospitalizations and even death from this, especially among high-risk groups.
Health effects resulting from exposure to the hot weather and what are the health effects associated with the heat?
Hot weather is a physical stress on the human body. Health effects are a variety of simple (mild) to such severe heat stroke, which can cause death.
To read more, please download here.
The Rise of Typhoid Fever in Klang Valley (Demam Kepialu)
Dear Staff and Students,
The Ministry of Health Malaysia has announced that since the beginning of August 2015, there were about seven (7) cases reported. Just recently there has been an increase of the dreaded typhoid fever in Klang Valley with 32 cases reported by both private and government hospitals. Areas affected are Titiwangsa, Kepong, Lembah Pantai and Cheras.
What is typhoid fever?
It is an infectious bacterial fever with an eruption of red spots on the chest and abdomen and severe intestinal irritation. It is a bacterial infection that can easily spread throughout the body through contaminated food and water or close contact, affecting many organs.Without prompt treatment, it can cause serious complications and can be fatal.
How does the typhoid fever spread?
You can get typhoid fever if you eat food or drink beverages that have been handled by a person who is shedding SalmonellaTyphi or if sewage contaminated with Salmonella Typhi bacteria gets into the water you use for drinking or washing food. Therefore, typhoid fever is more common in areas of the world where handwashing is less frequent and water is likely to be contaminated with sewage.
Once Salmonella Typhi bacteria are eaten or drunk, they multiply and spread into the bloodstream. The body reacts with fever and other signs and symptoms.
How can you avoid typhoid fever?
Two basic actions can protect you from typhoid fever:
- Avoid risky foods and drinks.
- Get vaccinated against typhoid fever.
It may surprise you, but watching what you eat and drink when you travel is as important as being vaccinated. This is because the vaccines are not completely effective. Avoiding risky foods will also help protect you from other illnesses, including travelers' diarrhea, cholera, dysentery, and hepatitis A.
"Boil it, cook it, peel it, or forget it"
- If you drink water, buy it bottled or bring it to a rolling boil for 1 minute before you drink it. Bottled carbonated water is safer than uncarbonated water.
- Ask for drinks without ice unless the ice is made from bottled or boiled water. Avoid popsicles and flavored ices that may have been made with contaminated water.
- Eat foods that have been thoroughly cooked and that are still hot and steaming.
- Avoid raw vegetables and fruits that cannot be peeled. Vegetables like lettuce are easily contaminated and are very hard to wash well.
- When you eat raw fruit or vegetables that can be peeled, peel them yourself. (Wash your hands with soap first.) Do not eat the peelings.
- Avoid foods and beverages from street vendors. It is difficult for food to be kept clean on the street, and many travelers get sick from food bought from street vendors.
What are the signs and symptoms of typhoid fever?
Persons with typhoid fever usually have a sustained fever as high as 103° to 104° F (39° to 40° C). They may also feel weak, or have stomach pains, headache, or loss of appetite. In some cases, patients have a rash of flat, rose-colored spots. The only way to know for sure if an illness is typhoid fever is to have samples of stool or blood tested for the presence of SalmonellaTyphi. If you have such manifestations, see a doctor immediately.
How to treat typhoid fever?
The typhoid fever is treatable by a medical professional. Treatment includes antiboitics and fluids.
Click on video url and see how the typhoid fever affects thebody:https://youtu.be/ON6A9kueUjQ
Department of Student Affairs
Sungai Long and Kampar Campus es
review YouTube video How Typhoid Fever Affects the Body -- The Doctors
Many thanks
THE HAZE
How to manage the haze situation?
Many of us have been affected by the haze which has reached very high levels in recent days. This page aims to give some straightforward facts and practical advice to help you cope with this problem.
Haze – what can we do?
The haze phenomenon has hit Malaysia again due to the hot spots in Sumatera. The haze contains smoke and dust particles and lingers in the air resulting in reduced visibility. When it comes into contact with the body, it can produce symptoms to the eyes, skin and breathing systems. The higher the API number is, the worse the haze and the implications to our health.
Symptoms that can occur when in contact with haze:
- Eye irritation
- Skin irritation
- Breathing problems: cough, shortness of breath, chest discomfort or tightness
- Throat discomfort and dryness. In people who are susceptible, the haze may cause worse symptoms or aggravation of pre-existing conditions like asthma and others
People who are susceptible:
- Known to have respiratory illnesses such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Known to have heart disease such as heart failure or coronary artery disease
- Small children, babies and the elderly
- Smokers
- Pregnant ladies
- People with allergies
Ways to minimize effects of haze to our body:
- Drink plenty of plain water and wash our faces frequently
- Minimise outdoor activities
- Avoid smoking and cigarette smoke
- When driving, close all windows and activate recycle air mode
- Close all house windows
- Use a mask that can cover the mouth and nose properly if there is a need to be outdoor
People who develop breathing difficulties or excessive cough should seek prompt medical attention. Patients who are known to have medical illnesses should take their medications as prescribed by their doctors. Patients with asthma who are on inhalers should continue taking their preventative medications and carry their reliever medication with them at all times. This is a good time for smokers to stop smoking completely, too.
To download this article, click here
Thank you
Department of Student Affairs
Sg Long & Kampar Campuses.
HAPUSKAN AEDES, CEGAH DENGGI



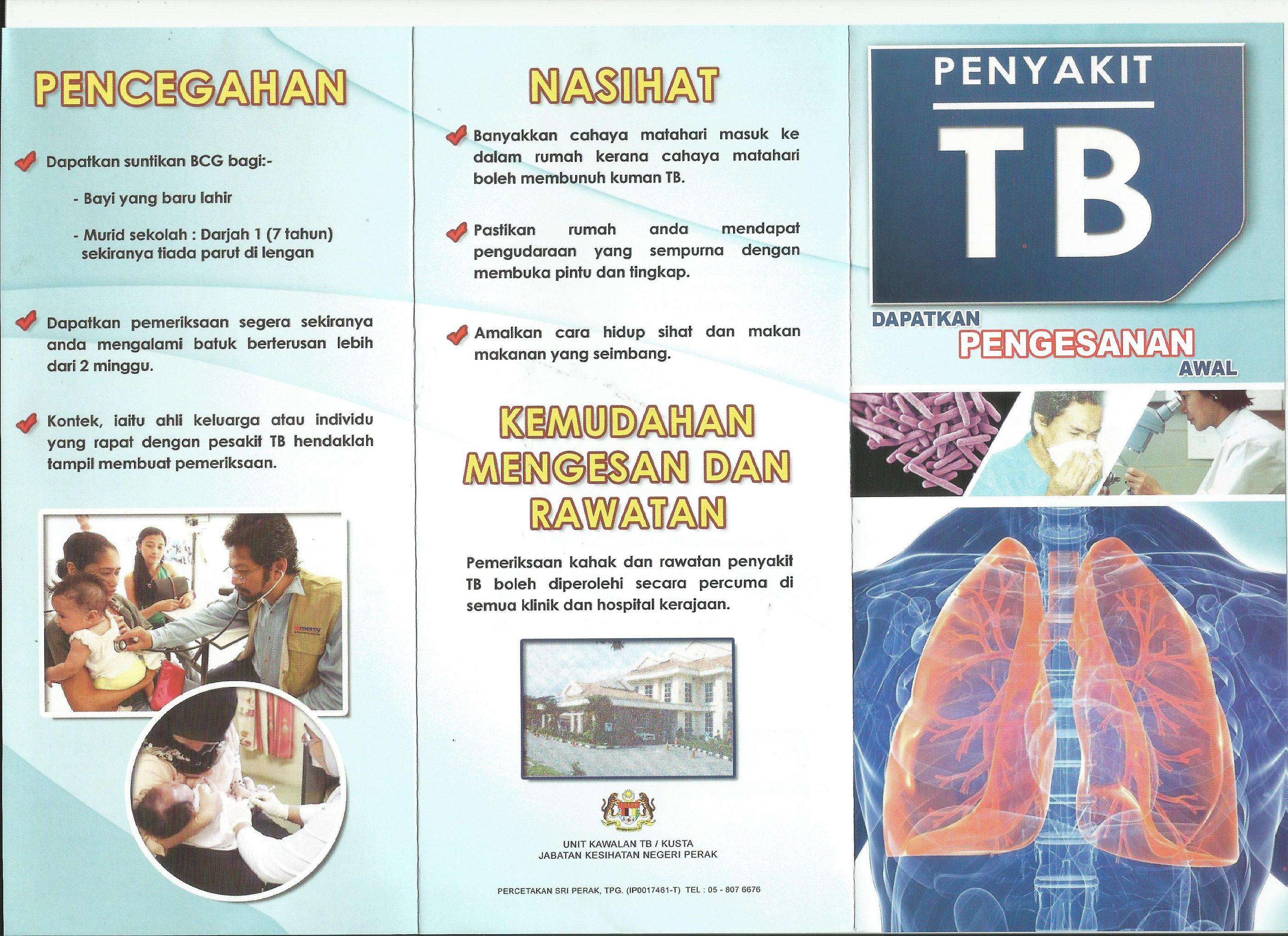
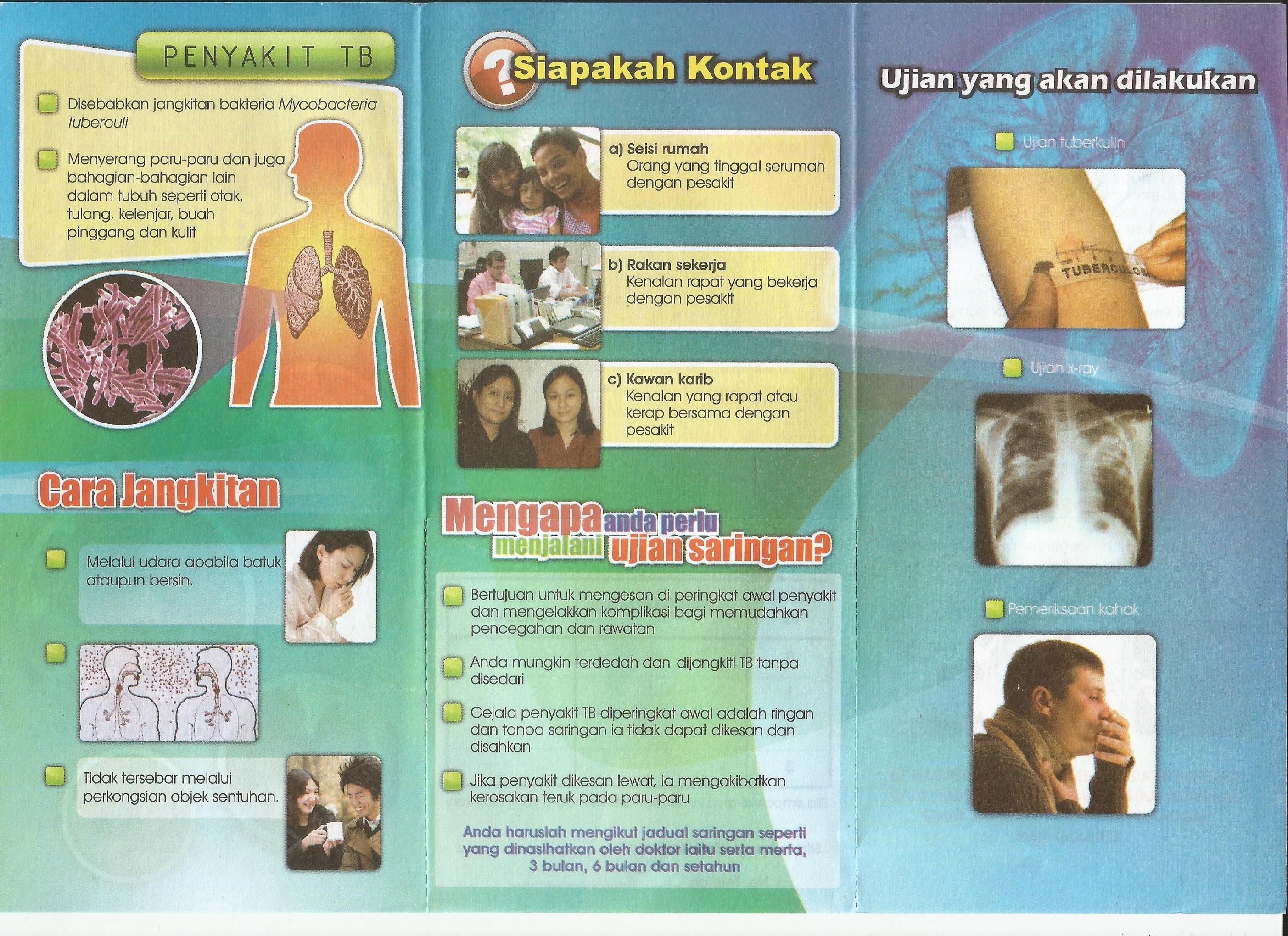
UNDERSTAND AND PREVENT FROM TUBERCULOSIS
Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever
Subject: HEALTH PRECAUTIONS
Greetings.
It is good that we remind ourselves of some everyday health precautions that all of us can take to ensure that all of us end this year healthily, and happily.
Dengue Fever, and Malaria are two examples of mosquito-borne diseases that can be prevented if we practice good hygiene, such as ensuring that our environment is well kept (i.e. no rubbish strewn around), and making sure that garden pots and rubbish bins do not contain stagnant water.
Constant and regular contact with people especially in our campuses where there is a large and frequent movement of people from one locality to another is also a potential risk for infectious diseases such as Tuberculosis, or TB.
Leptospirosis, caused by rat urine, is also potentially dangerous if your environment is not clean (i.e. rubbish strewn around, which attracts rats into your area).
All UTARians are advised to take normal, everyday steps to improve hygiene, such as regular washing of hands, and coughing or sneezing into a piece of tissue.
These and other infectious diseases can be prevented if you take the proactive approach to good health:
- Do not take things for granted. If you have prolonged or serious symptoms such as
COUGHING for MORE THAN FEW DAYS, FEVER, DIARRHEA or LOSS OF WEIGHT AND APPETTITE, go to the nearest GOVERNMENT HOSPITAL or clinics where tests can be done to determine what illness you are having
- Practice GOOD HYGIENE
- CLEAN YOUR ENVIRONMENT - do not let rubbish be strewn around.
- Go for vaccinations which are available free in government clinics and hospitals. Seek advice on this from the hospitals and clinics.
You are strongly advised and encouraged to do your part to make Malaysia and the UTAR campuses a healthier place to live in.
Thank you.
Department of Student Affairs
22 October 2013
Other Brochures
- SIRI MAKAN SECARA SIHAT 1 2 3 4
- 10,000 Steps A Day for Healthy Living 1 2
- Diabetes Prevention 1 2
- Healthy Weight 1 2
- Saringan Kontak Untuk TB 1 2
- SIHAT TANPA ALKOHOL 1 2
- UJIAN HIV TANPA NAMA 1 2